Diagnostic Monitors
Home » Products » High-Tech LCD Monitors » Diagnostic Monitors
Diagnostic imaging demands absolute consistency: stable luminance, accurate grayscale rendering, and repeatable calibration so subtle findings don’t get lost. These diagnostic monitors are built around embedded sensing, uniformity control, and workflow-focused features (like reading lights and presence detection) to support long reading sessions and high-throughput environments.
Features
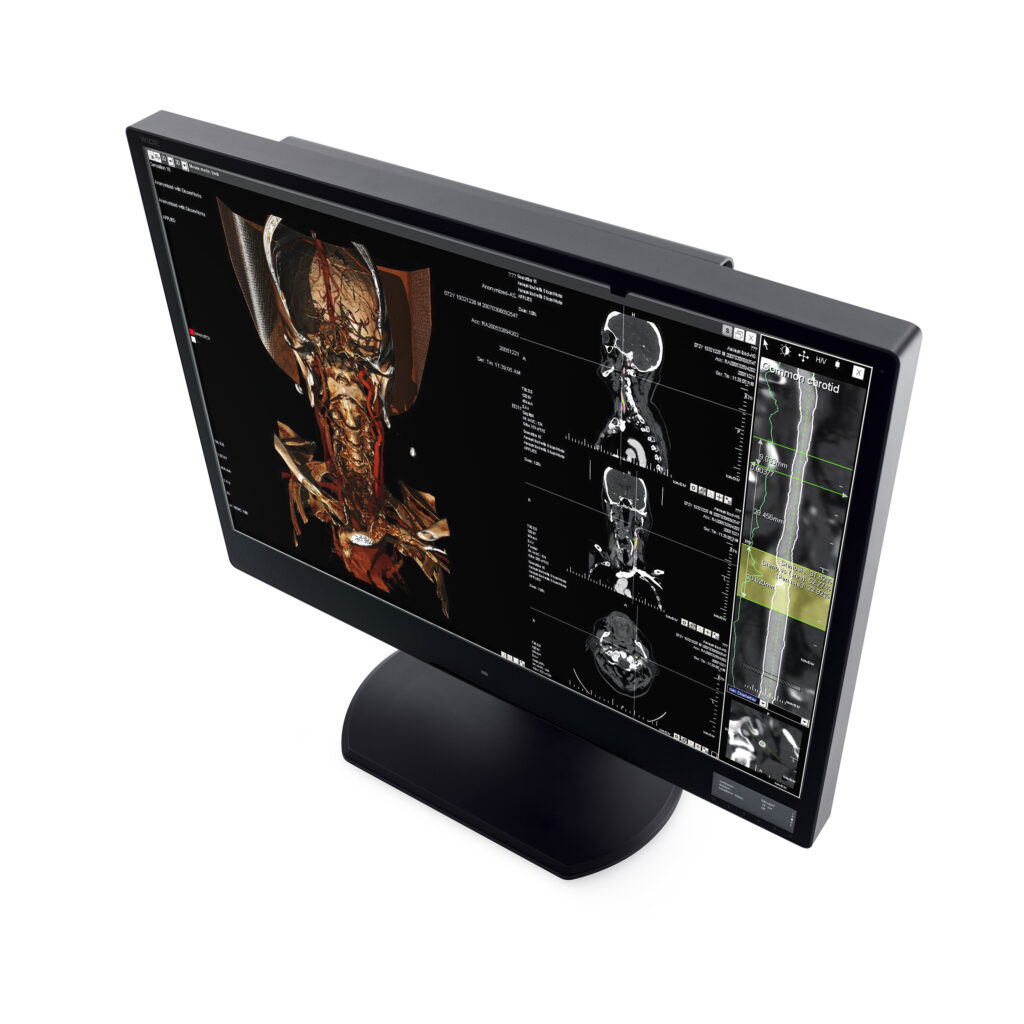
Diagnostic models in this family are designed to help maintain image quality over time with integrated sensors and calibration/QA support. For example, the CW120N (12MP) includes an embedded IQ sensor, ambient sensor, human detection, and self DICOM calibration/conformance features, plus task lighting options.
The Diagnostic lineup provides:
High precision grayscale rendering (e.g., 14-bit LUT / grayscale support on several models) for confident interpretation of fine detail.
Embedded sensing + stability controls (e.g., IQ sensor / SBC / ambient & human sensors depending on model) to help maintain target luminance performance.
Uniformity and ambient-response tools (e.g., LUC / DAC on certain diagnostic models) to support consistent viewing across the panel and conditions.
Workflow enhancements on flagship models (reading light, dual DP inputs, private menu screen, motion sensor) to reduce friction during long sessions.
Calibration & QA software support for DICOM GSDF and broader medical display QA activities.
About
How the technology works
These diagnostic monitors pair on-screen performance controls with measurement and calibration tools. A common approach described for this ecosystem is an Image Quality Assurance System that combines an embedded sensor, self-brightness control, and bundled DICOM calibration software to automate calibration and conformance tasks (including DICOM 3.14 calibration/conformance).
For deeper QA workflows, the calibration suite documentation describes support for calibration to NEMA DICOM Part 14 GSDF and verification/conformance activities aligned with multiple medical standards, along with reporting and scheduling/reminders.
Advantages and limitations
Advantages include tighter consistency across workstations, less manual drift management, and a more repeatable path to maintaining target display behavior over time (especially when QA schedules and reporting are used).
Limitations are mostly operational: achieving best results still depends on having a clear QA process (who runs tests, how often, and what thresholds trigger corrective action) and a workstation setup capable of driving very high resolutions where applicable.
Applications
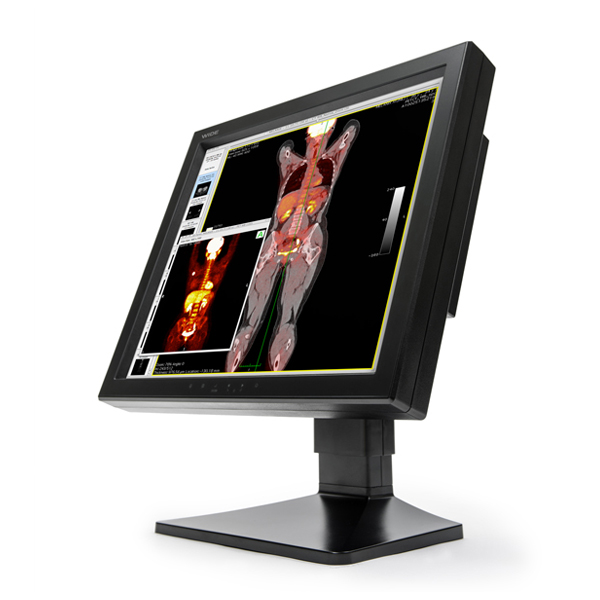
Radiology reading rooms (multi-modality review)
Mammography / tomosynthesis workflows (where supported by model selection)
Any environment requiring repeatable DICOM-oriented calibration and monitor QA
Conclusion
Diagnostic monitors aren’t “just displays”—they’re part of an image-quality system. With embedded sensors, uniformity/ambient controls, and calibration + QA software support, this lineup is built to help teams keep performance consistent and auditable as workloads scale.