Heatsinks
In the world of electronics, managing heat is a critical aspect that should not be overlooked. The heat generated by electronic components can affect their performance and lifespan, leading to serious problems such as overheating and malfunctioning. One of the most effective solutions to manage heat is by using heatsinks. A heatsink is a passive cooling device that dissipates heat away from electronic components and regulates their temperature. In this article, we will discuss how heatsinks work, their advantages and limitations, and their applications.
About
How the technology works
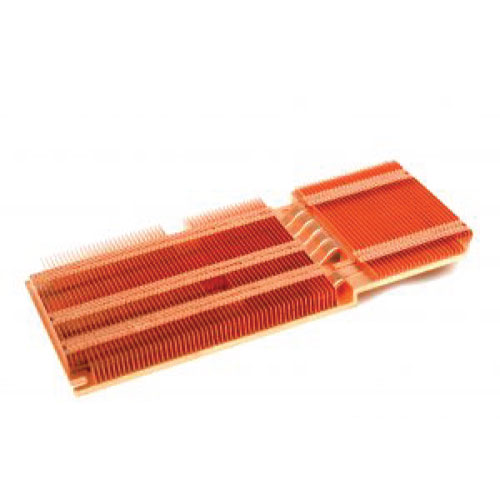
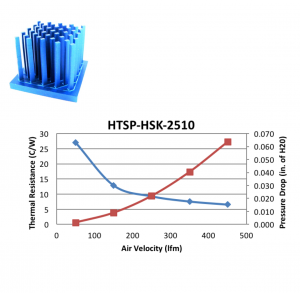
The basic principle behind heatsinks is the transfer of heat from a hot component to a larger surface area, where it can be dissipated into the air more efficiently. Heatsinks are typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, and feature a series of fins or ridges that increase their surface area.
When an electronic component generates heat, the heatsink absorbs it and transfers it to its fins or ridges. The increased surface area of the heatsink allows the heat to be dissipated into the surrounding air through convection. In some cases, fans or other active cooling methods can be used to enhance the efficiency of the heatsink.
Advantages and limitations
The use of heatsinks in electronic devices offers several advantages. First, they help to regulate the temperature of electronic components, which can improve their performance and lifespan. Second, they are a cost-effective solution for managing heat, as they are passive devices that do not require additional power. Third, they are easy to install and require little maintenance.
However, there are also some limitations to the use of heatsinks. First, they are not effective in managing heat in high-temperature environments or under conditions of high power dissipation. Second, they may not be suitable for devices with limited space, as heatsinks can be bulky and require additional clearance. Third, the efficiency of a heatsink can be affected by factors such as airflow, orientation, and contact with the component.
Applications
Heatsinks are commonly used in a variety of electronic devices, including computers, power supplies, LED lights, and audio amplifiers. They are also used in automotive and aerospace applications, where managing heat is critical for ensuring the reliability and safety of electronic systems. In addition, heatsinks are used in renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to manage heat generated by power electronics.
Conclusion
Heatsinks are a critical component of electronic systems that help to manage heat and improve performance and lifespan. They work by transferring heat from electronic components to a larger surface area, where it can be dissipated into the air more efficiently. Although there are some limitations to the use of heatsinks, they are a cost-effective and reliable solution for managing heat in a variety of applications. As electronic systems continue to become more powerful and compact, the use of heatsinks will become increasingly important for ensuring their reliability and performance.